Foster Kennedy Syndrome Symptoms
Foster kennedy syndrome symptoms. Was first described in 1911. Subfrontal meningioma resulting in. Early symptoms include tremor of the outstretched hands muscle cramps with exertion and fasciculations fleeting muscle twitches visible under the skin.
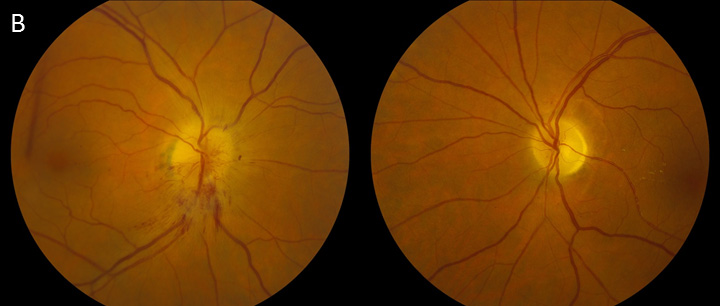
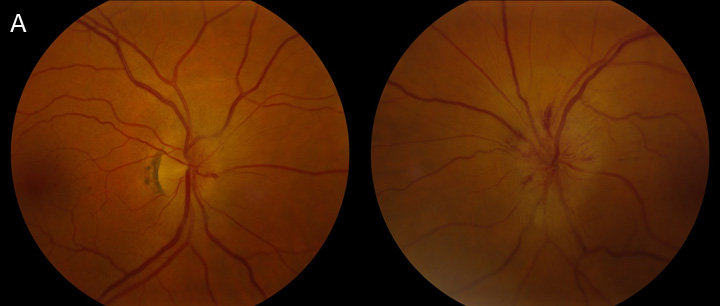
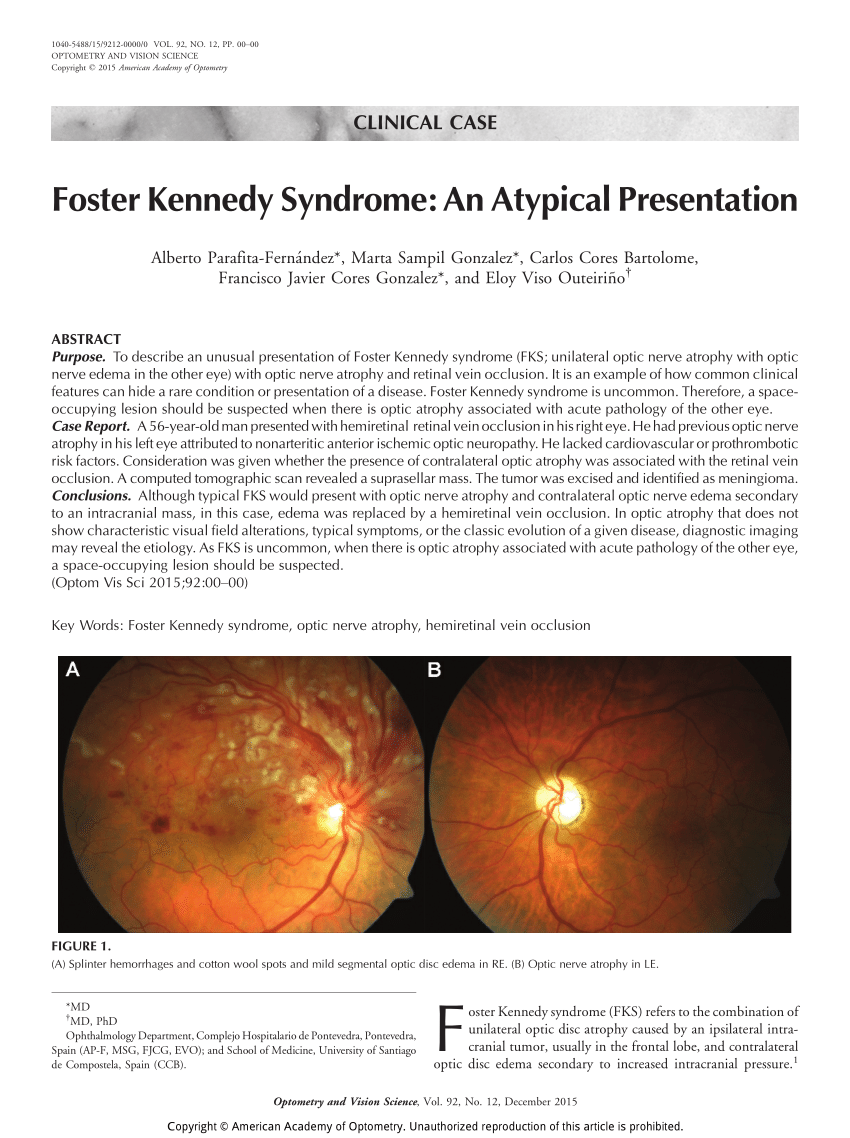
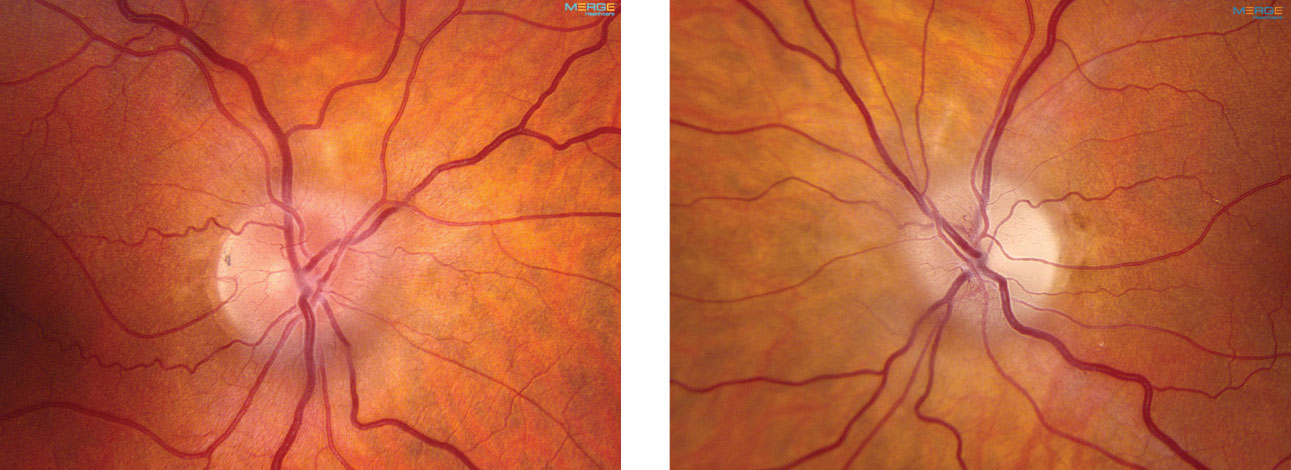
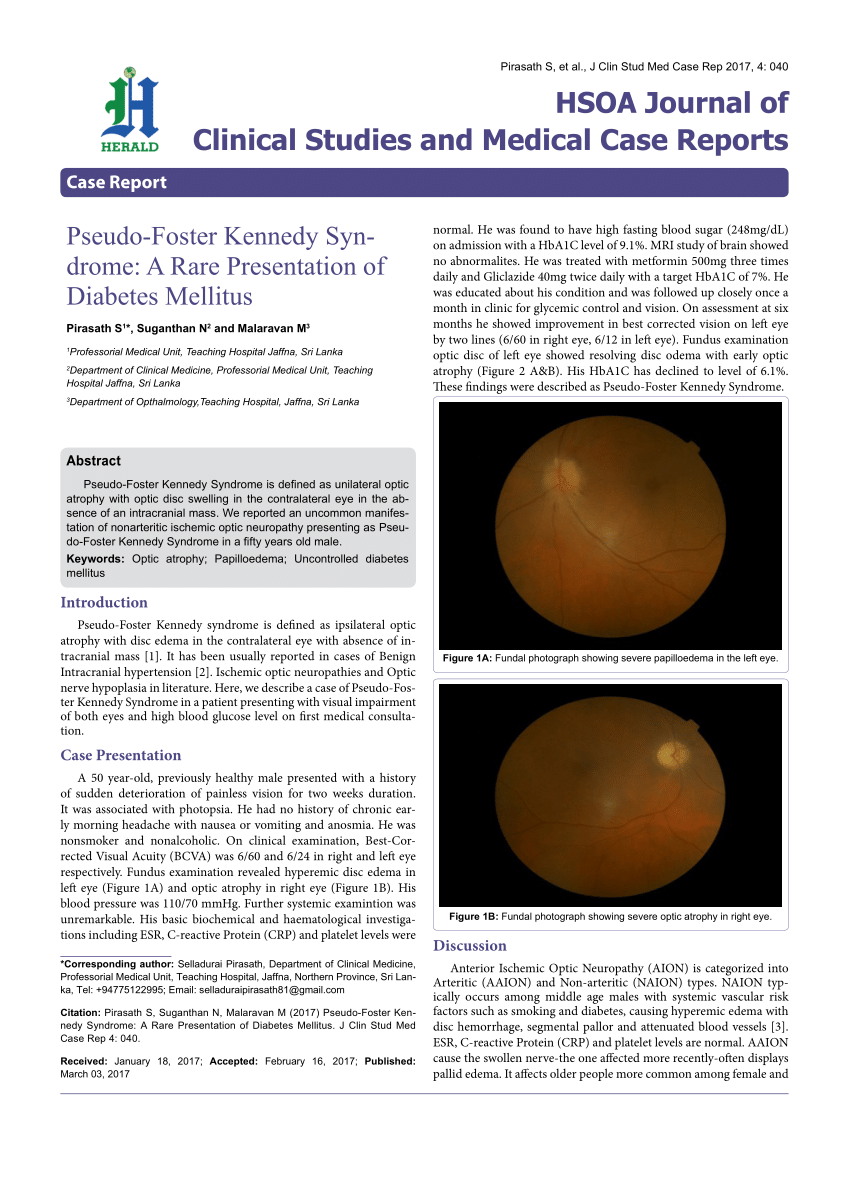
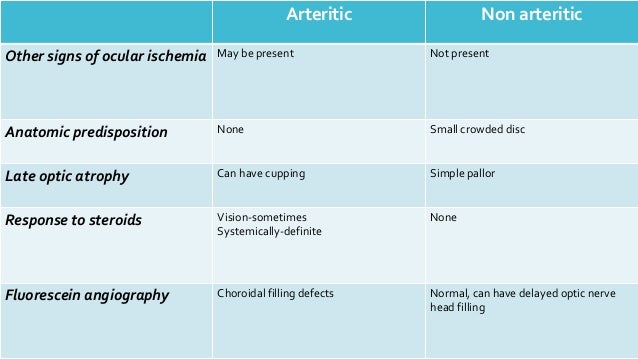
Although many of these symptoms regularly co-occur it is common to encounter patients who have several but not all of these symptoms. Optic atrophy Loss of fibers of optic nerve Papilledema Optic disc swelling due to intracranial pressure Central scotoma Alteration of center field of vision Anosmia loss of smell. He initially presented with acute vision loss in the left eye and was noted to have disc edema with peripapillary hemorrhages OS and trace hyperemic disc edema OD A from non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy NAION OS and incipient NAION OD.
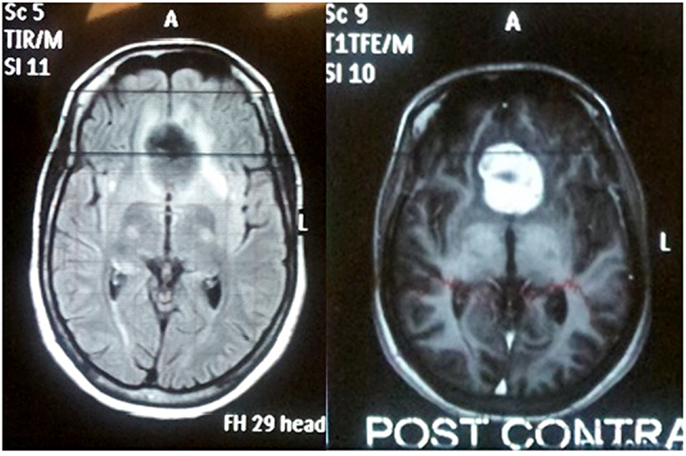
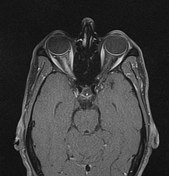
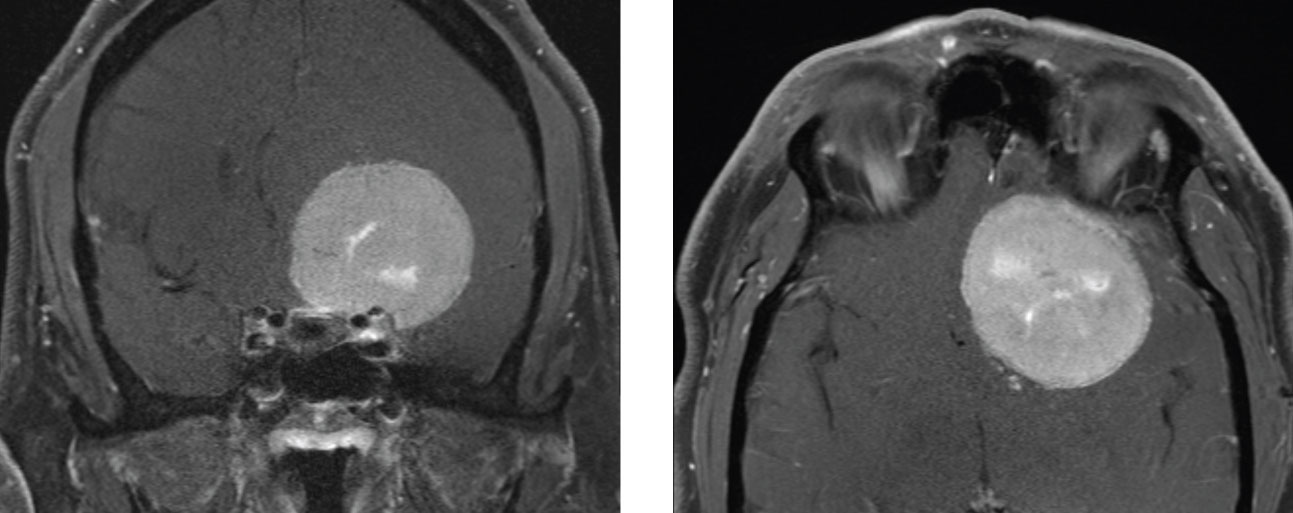
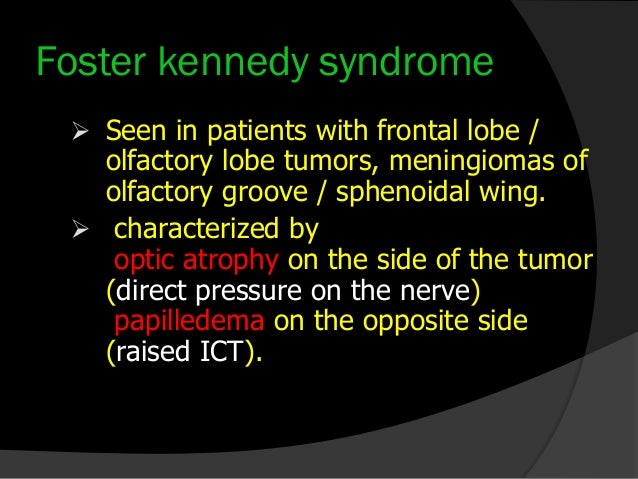
Foster Kennedy who char-. 2 Tumours of the frontal lobe can become quite large before they are discovered and focal symptoms eg memory loss or emotional lability may be sparse. 10 This has the clinical appearance of optic atrophy in one eye and papillitis in the fellow eye in the absence of cranial mass.
Intracranial pressure causing contra-. Possible causes include Meningioma. Other neuro-ophthalmologic signs and symptoms include poor color perception an afferent pupillary light defect abnormal visual fields 80 pallor of the optic discs 83 the Foster-Kennedy syndrome 72 and abnormal extraocular movements 36.
Talk to our Chatbot to narrow down your search. Cognitive movement and speech emotional or behavioral. Eventually individuals develop limb weakness which usually begins in the pelvic or shoulder regions.
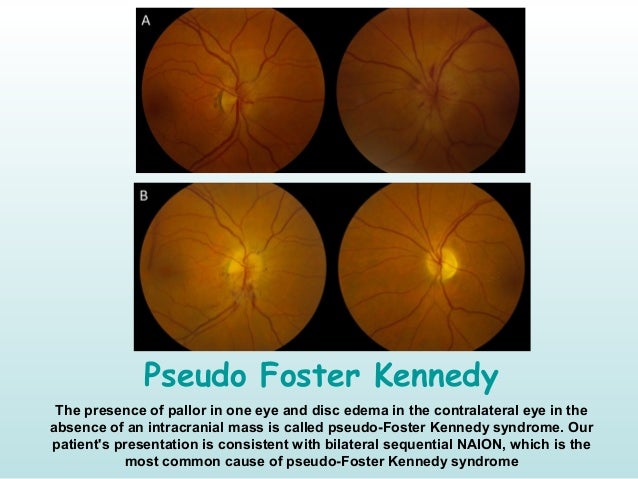
Headache is also common being found in 3555 of the patients. If symptoms are ignored or the diagnosis for GCA is overlooked the patient may later present with pseudo-Foster-Kennedy syndrome. Broadly speaking these symptoms fall into three main categories.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as muscle weakness and cramps in the arms legs and facial area enlarged breasts and difficulty with speaking and swallowing dysphagia. Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now.
Optic nerve head pallor with increased.
Headache is also common being found in 3555 of the patients. By the neurologist Robert. Optic nerve head pallor with increased. Foster-Kennedy syndrome. Acterized the disorder as. Although many of these symptoms regularly co-occur it is common to encounter patients who have several but not all of these symptoms. Eventually individuals develop limb weakness which usually begins in the pelvic or shoulder regions. Other neuro-ophthalmologic signs and symptoms include poor color perception an afferent pupillary light defect abnormal visual fields 80 pallor of the optic discs 83 the Foster-Kennedy syndrome 72 and abnormal extraocular movements 36. Download PDF Foster Kennedy syndrome was first described in 1911 by the neurologist Robert Foster Kennedy who characterized the disorder as compression of one optic nerve by a subfrontal meningioma resulting in optic nerve head pallor with increased intracranial pressure causing contralateral optic nerve head edema.
Download PDF Foster Kennedy syndrome was first described in 1911 by the neurologist Robert Foster Kennedy who characterized the disorder as compression of one optic nerve by a subfrontal meningioma resulting in optic nerve head pallor with increased intracranial pressure causing contralateral optic nerve head edema. Was first described in 1911. By the neurologist Robert. Early symptoms include tremor of the outstretched hands muscle cramps with exertion and fasciculations fleeting muscle twitches visible under the skin. Eventually individuals develop limb weakness which usually begins in the pelvic or shoulder regions. Although many of these symptoms regularly co-occur it is common to encounter patients who have several but not all of these symptoms. Possible causes include Meningioma.

































Post a Comment for "Foster Kennedy Syndrome Symptoms"