Down Syndrome Atlantoaxial Instability
Down syndrome atlantoaxial instability. Atlanto-axial instability in children with Down syndrome. In people with Downs syndrome the ligaments which normally hold the joints stable can be very slack. The potential subluxation of the C1-C2 verte-.
Difficulty nodding or looking up and down andor difficulty turning the head in certain directions. In people with Down syndrome the ligaments connections between muscles are lax or floppy. Atlantoaxial Instability in Children with Down Syndrome Children with Down syndrome are at increased risk of developing compression of the spinal cord called atlantoaxial instability.
The joint between the upper spine and base of the skull is called the atlanto-axial joint. Tripping up or a jolt. Atlanto-axial instability AAI is a condition that affects the bones in the upper spine or neck under the base of the skull.
Atlanto-axial subluxation and cervical myelopathy in rheumatoid arthri-tis. The spinal cord can be pressed by the bones and cause nerve damage. Atlantoaxial instability Approximately 20 of patients with Down syndrome have ligamentous laxity of the atlantoaxial joint.
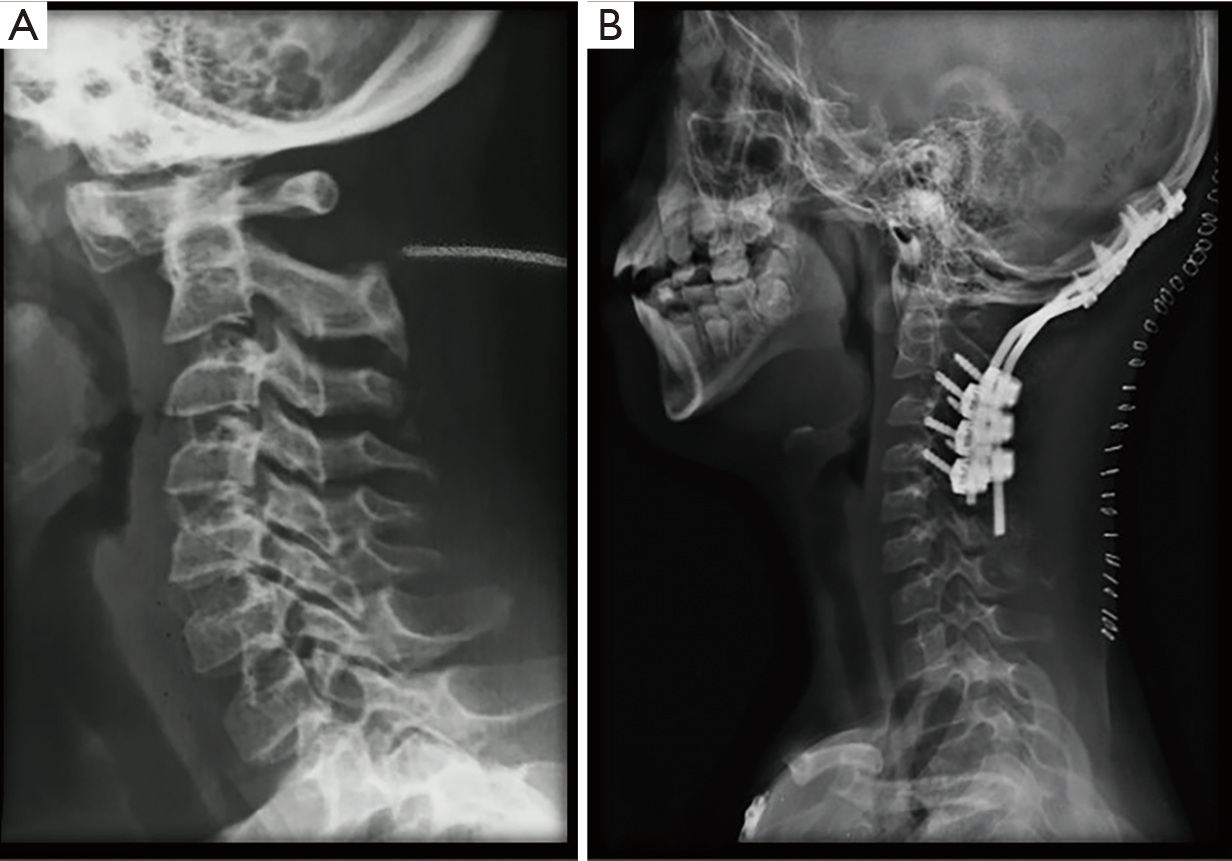
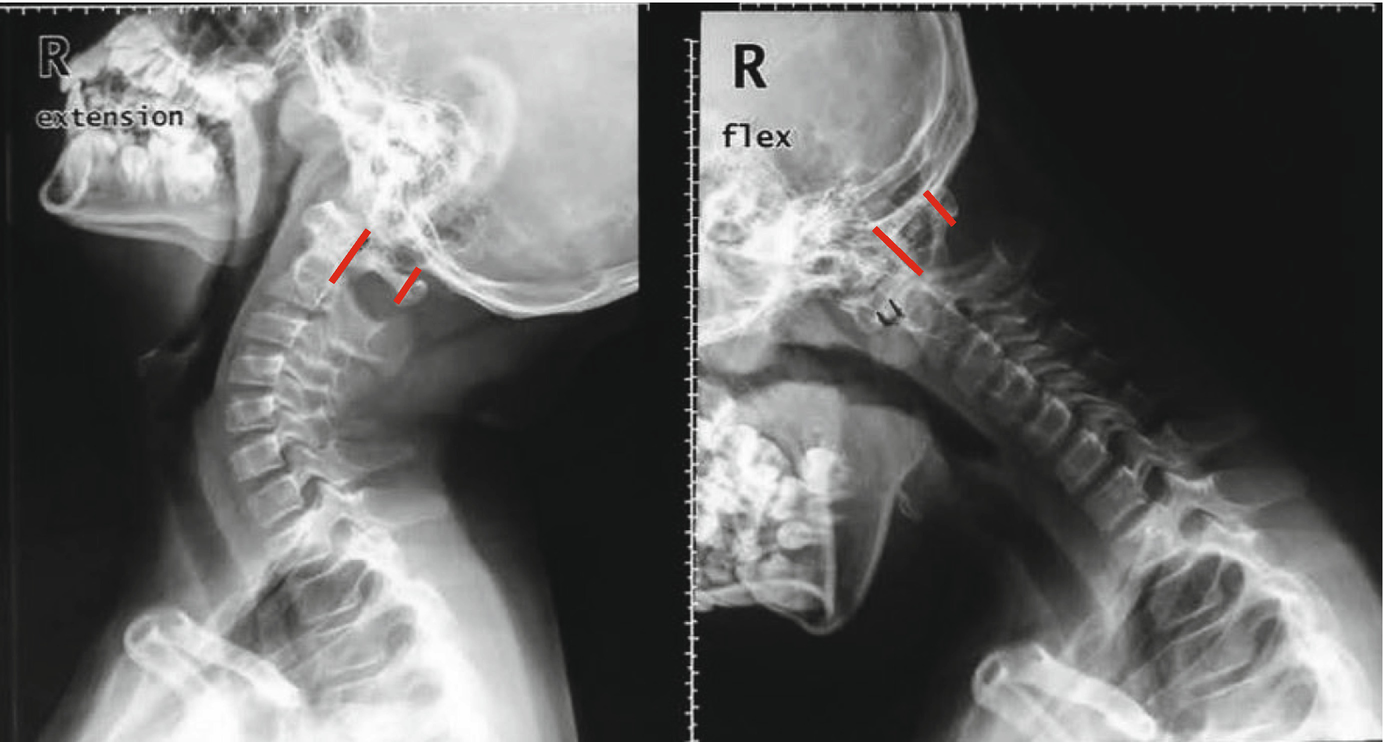
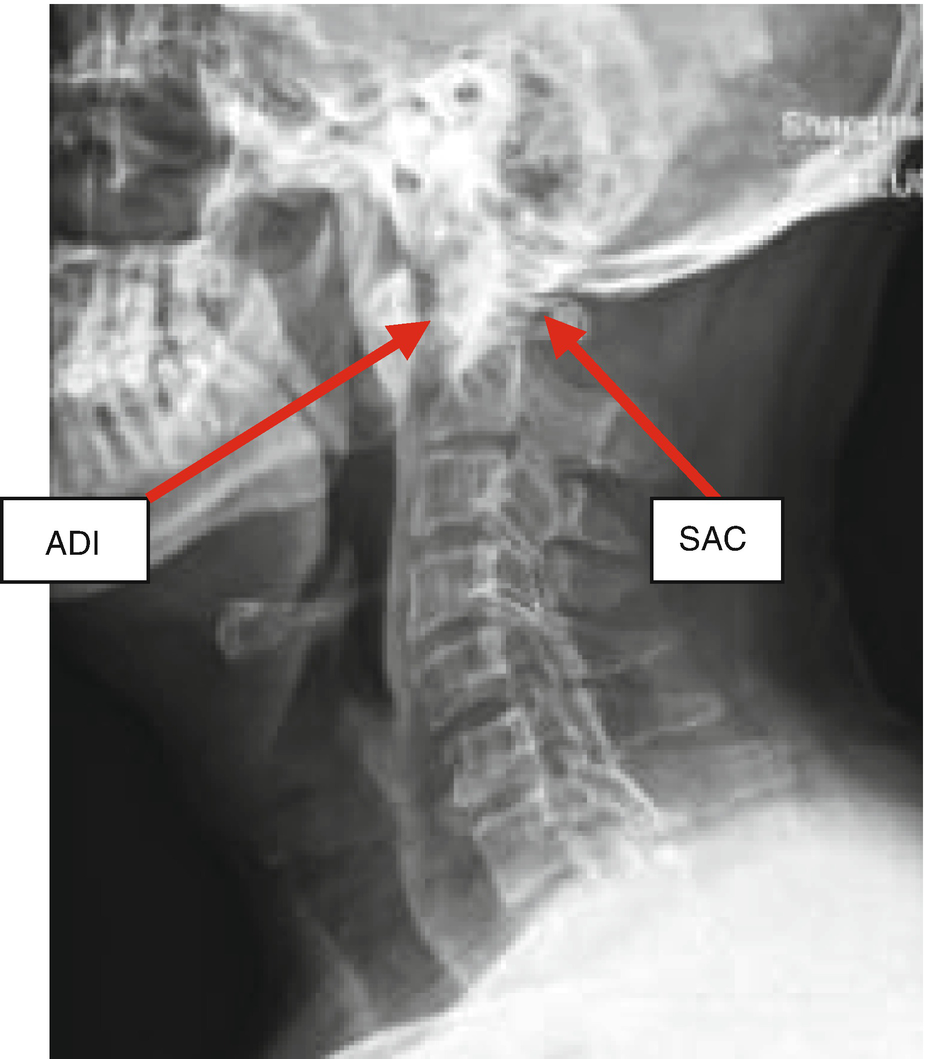
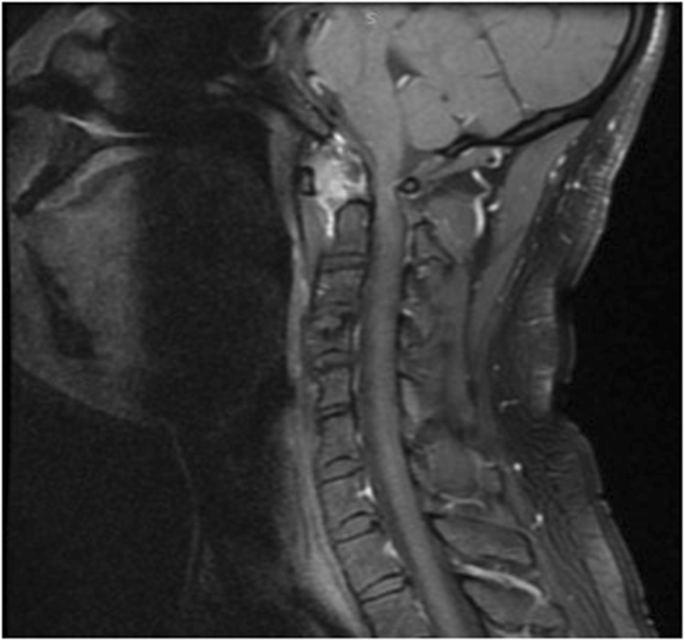
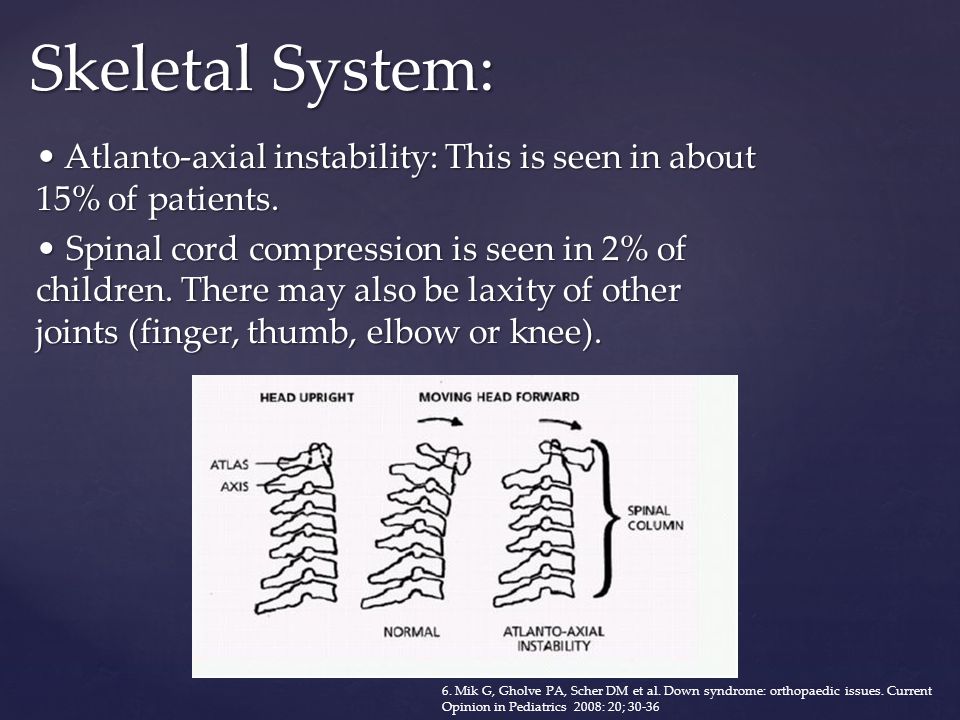
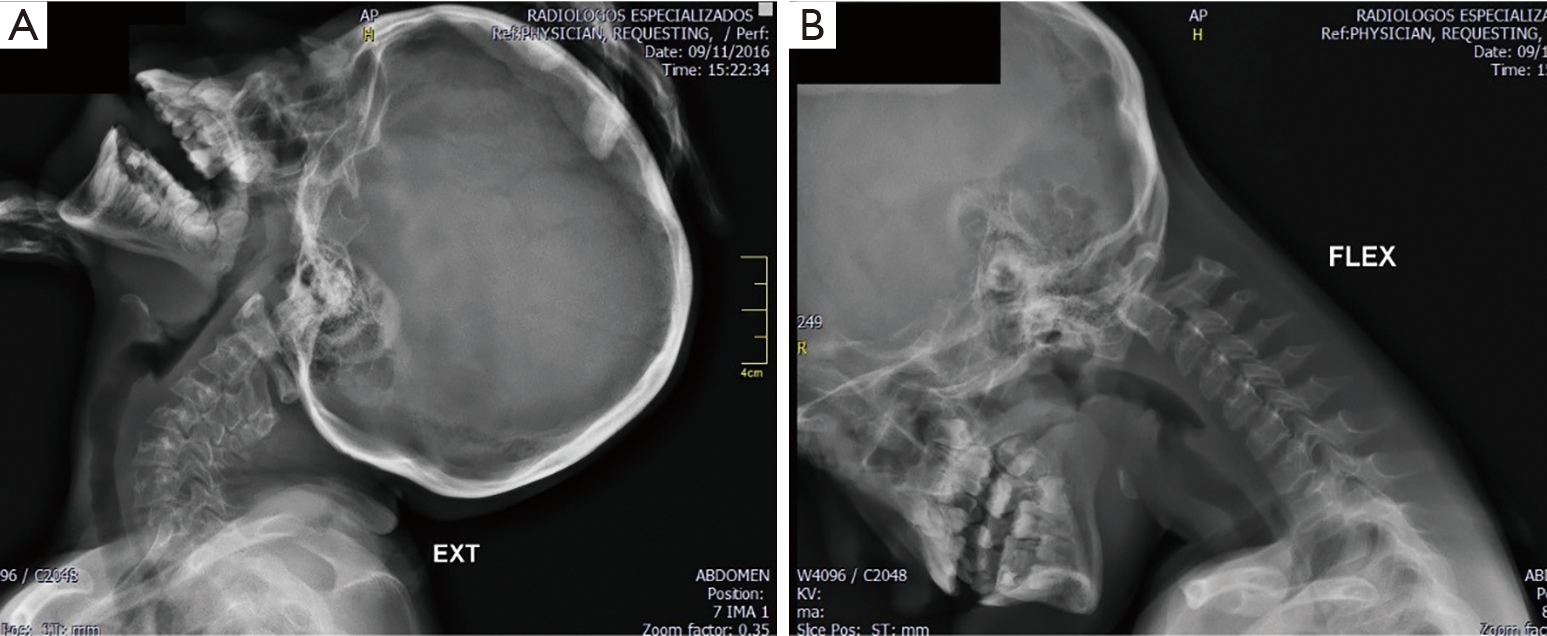
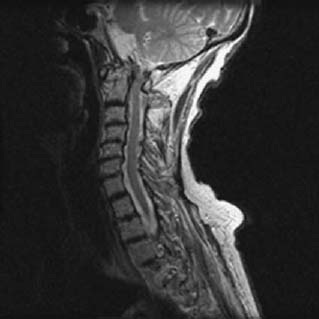
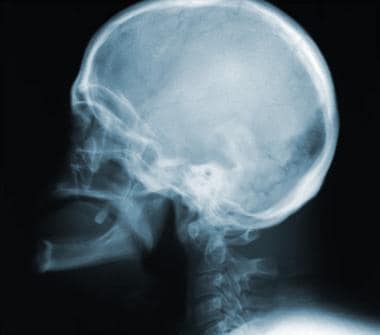
The incidence of atlantoaxial instability among persons with Down syndrome has been reported by various observers to be 10 to 20. When the distance on X-ray between the atlas 1st vertebra and odontoid process 2nd vertebra is more than 45 millimeters mm. 2915 When atlantoaxial instability results in subluxation or dislocation of C-1 and C-2 the spinal cord also may be injured.
There are potentially fatal consequences to performing adjustive manipulation to the cervical spine of the Downs patient. Dev Med Child Neurol 198325252-255 15. Atlantoaxial subluxation can cause death.
Atlantoaxial instability was radiologically identified by the space between the anterior border of the odontoid apophysis and the posterior border of the atlas arch as well as by the Wiesel-Rothman line. Normalities in Downs syndrome.
The spinal cord can be pressed by the bones and cause nerve damage.
There are potentially fatal consequences to performing adjustive manipulation to the cervical spine of the Downs patient. 2915 When atlantoaxial instability results in subluxation or dislocation of C-1 and C-2 the spinal cord also may be injured. However not until age 3 years will they have adequate vertebral mineralization and epiphyseal development for accurate radiographic evaluation of the cervical spine. This is a rare but serious complication. Children with Down syndrome are at increased risk of atlantoaxial instability. A chiropractic perspective on atlantoaxial instability in Downs syndrome. All children with Down syndrome who wish to participate in sports should have cervical spine X-rays. The incidence of atlantoaxial instability among persons with Down syndrome has been reported by various observers to be 10 to 20. In people with Down syndrome the ligaments connections between muscles are lax or floppy.
5 This condition may allow C1-C2 subluxation and predis-pose patients with Down syndrome to spinal cord injury. Atlanto-axial instability in children with Down syndrome. Instability in these areas is usually termed atlantooccipital instability and atlantoaxial instability AAI. Difficulty nodding or looking up and down andor difficulty turning the head in certain directions. In 1984 the AAP issued its first position statement on Atlantoaxial Instability AAI in children with Down syndrome. Causes of Craniocervical Instability in Down Syndrome Craniocervical instability in DS involves the occiputC1 or more commonly the C1C2 level. In people with Down syndrome the ligaments connections between muscles are lax or floppy.



























Post a Comment for "Down Syndrome Atlantoaxial Instability"