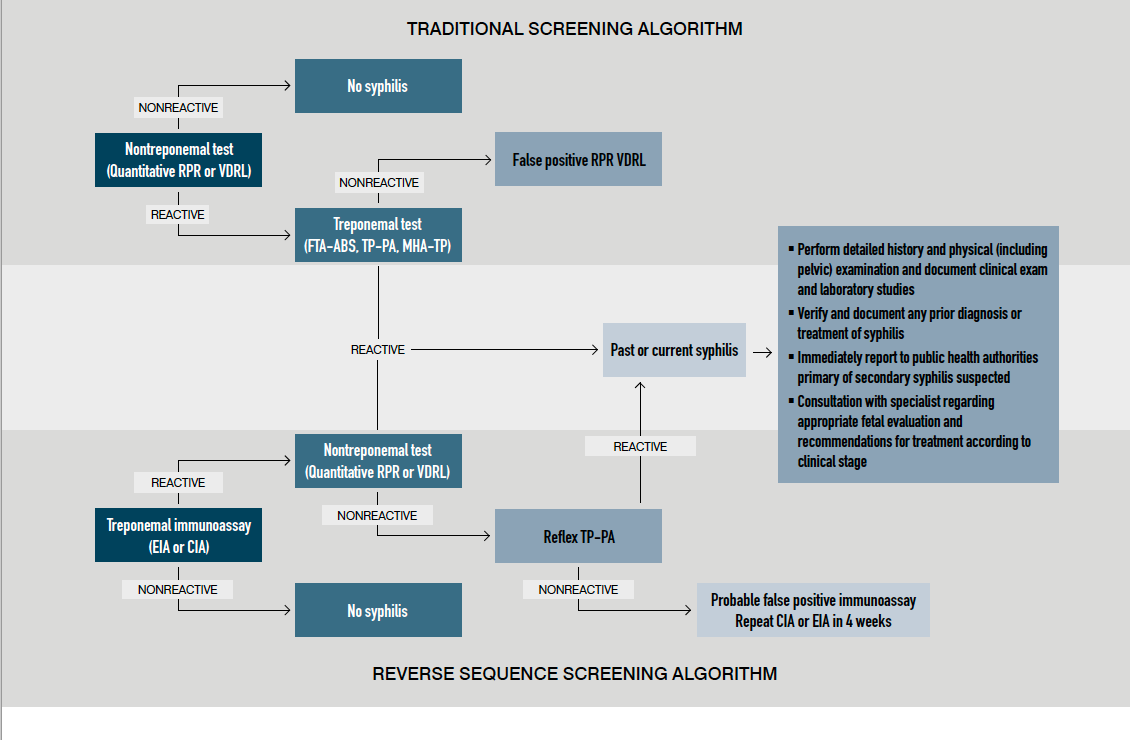
Syphilis Treatment In Pregnancy
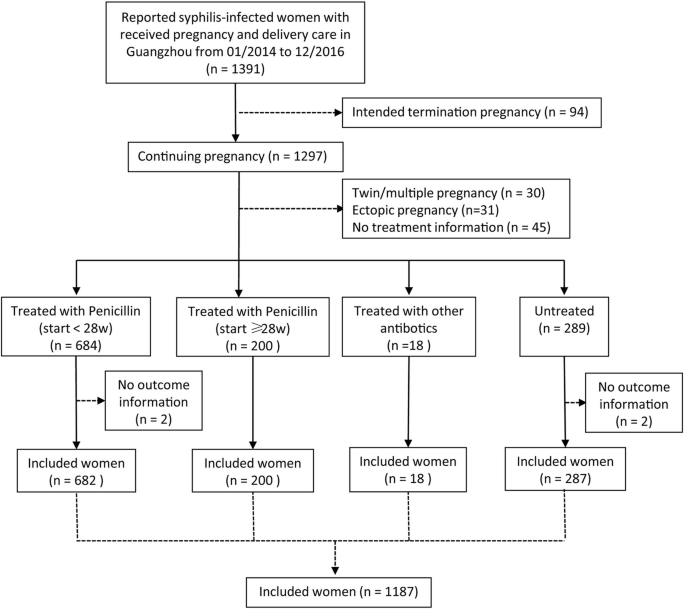
Syphilis treatment in pregnancy. In determining a penicillin regimen the clinician must consider the stage of the maternal infection and the HIV status of the mother. Congenital syphilis after maternal treatment for syphilis during pregnancy. Screening early in pregnancy repeat screening in the third trimester and at delivery among women at high risk adherence to recommended treatment regimens and prompt reporting of newly diagnosed syphilis cases to local public health authorities are strategies that obstetriciangynecologists can employ to fight the current epidemic.
65 Insufficient data exist to recommend azithromycin. Early detection and treatment in mothers. The value of penicillin alone in the prevention and treatment of congenital syphilis.
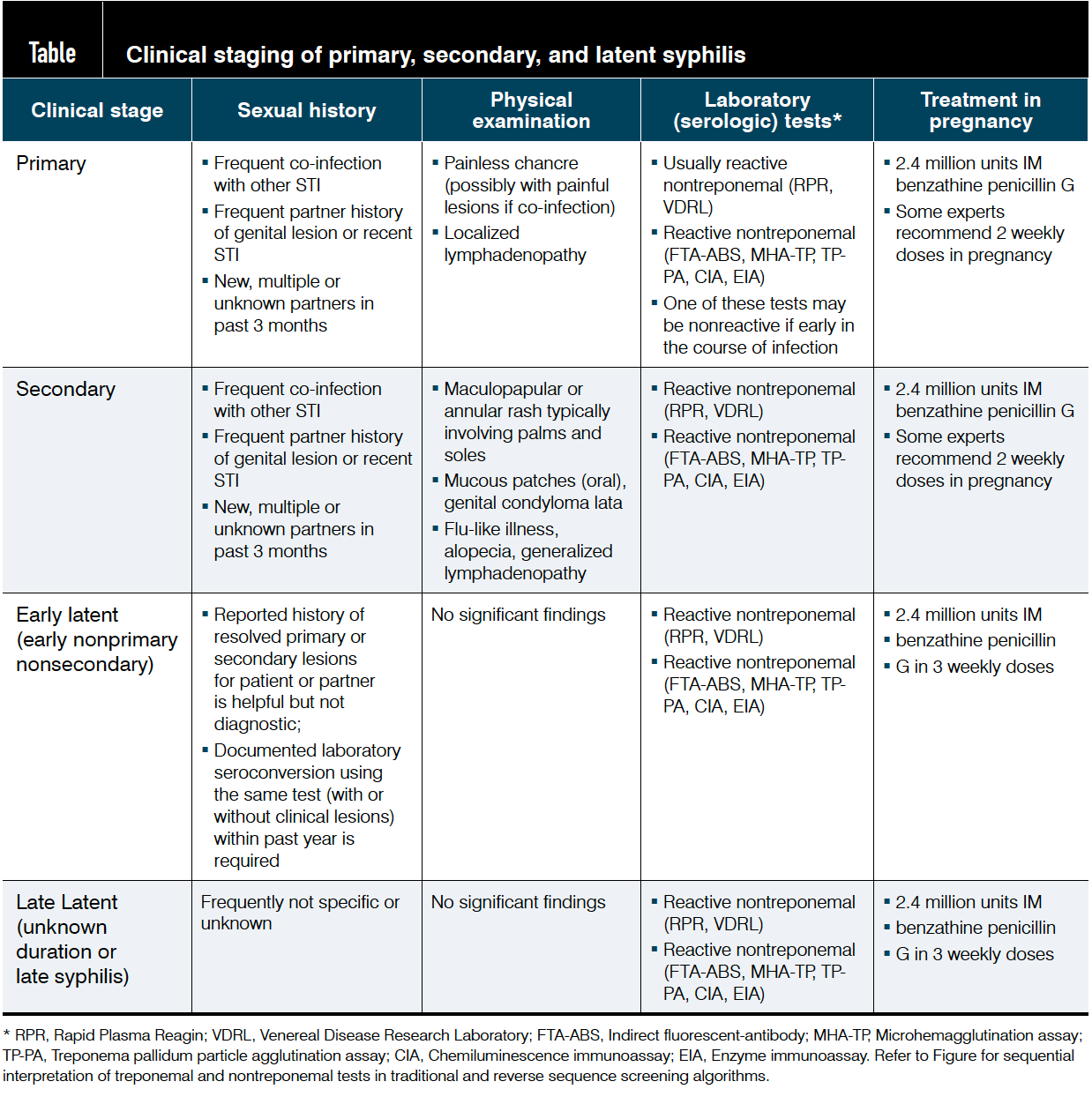
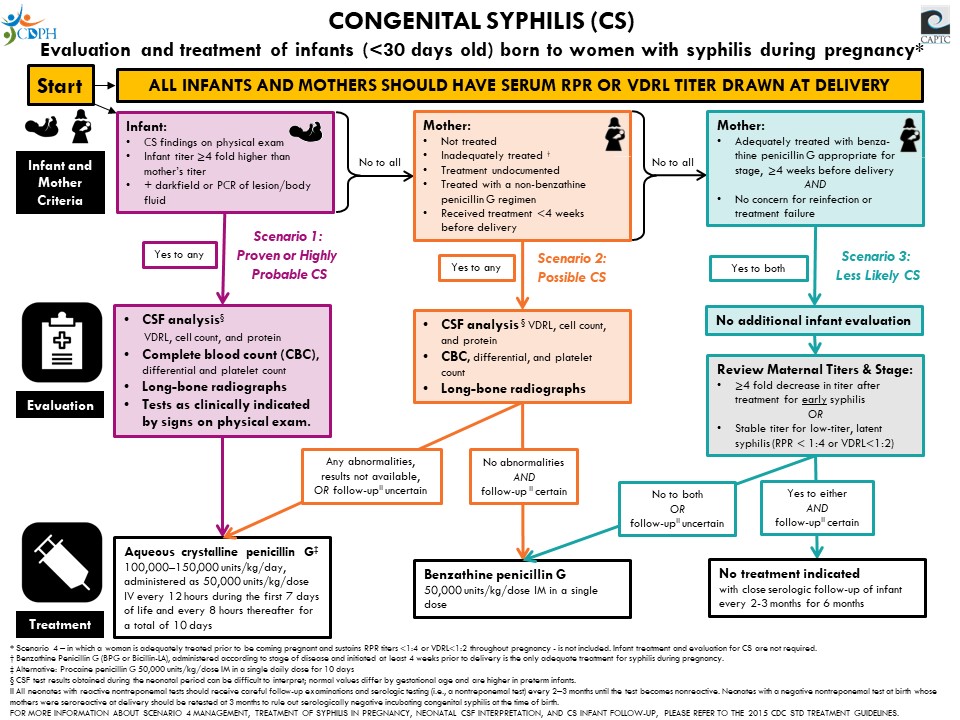
Management and treatment of syphilis in the pregnant woman andor her baby Additional investigations Consider FBC ELFT Chest x-ray Long bone radiographs CSF Neuroimaging Ophthalmologic exam Auditory brain stem response Treatment for congenital syphilis 07 days of age Benzyl penicillin 30 mgkg IV 12 hourly for 10 days. Fifteen 45 of the subjects had a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction including all three 12 of 20 60 and none of ten of those with primary secondary and latent syphilis respectively. Syphilis in pregnancy should be treated with the standard regimen used for the same clinical stage of syphilis in non-pregnant people.
The fetus can be easily cured with treatment and the risk of adverse outcomes to the fetus is minimal if the mother receives adequate treatment during early pregnancy ideally before the second trimester. 68 70 Tetracycline the only other agent that has been proved effective is not recommended because of dental staining and impairment of long bone growth in the fetus and hepatotoxicity when given intravenously to a pregnant women with coexisting renal insufficiency. Despite appropriate treatment as many as 14 will have a fetal death or deliver.
In the case of a confirmed diagnosis the pregnant woman should be hospitalized in dermatovenereologic hospital for treatment. If a pregnant woman has syphilis it can be transmitted to her baby. Treatment during pregnancy should be with penicillin.
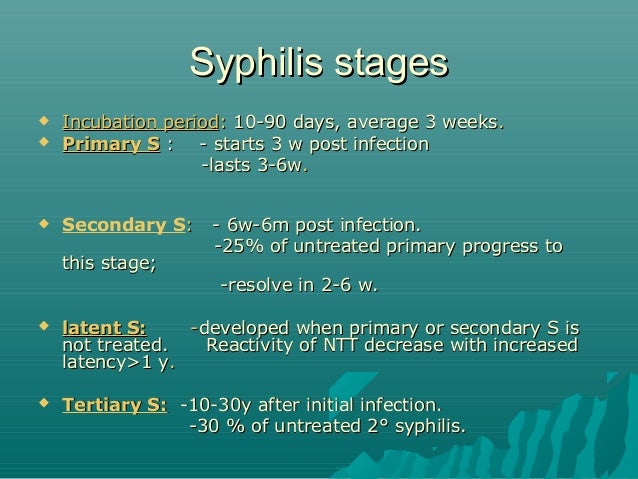
Latent asymptomatic syphilis infections in pregnancy also cause serious adverse pregnancy outcomes in more than half of cases. This guideline provides updated recommendations for syphilis screening and treatment for pregnant women based on. Syphilis in pregnancy can be safely treated with antibiotics which can prevent these complications.
Erythromycin is not recommended because it frequently fails to eradicate syphilis in both the mother and the fetus. In pregnancy it can result in spontaneous miscarriage or stillbirth or cause congenital syphilis infection.
The only exception is early syphilis diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy which should be treated with.
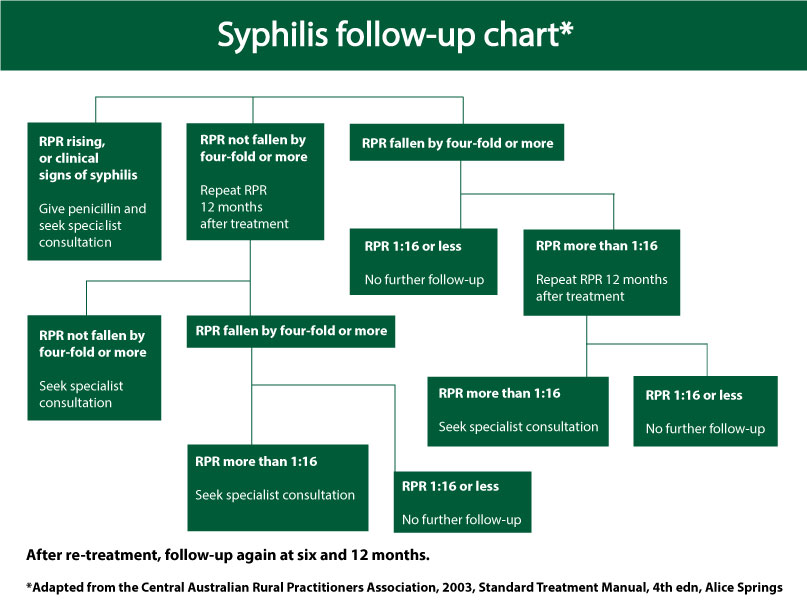
Congenital syphilis after maternal treatment for syphilis during pregnancy. Congenital syphilis after maternal treatment for syphilis during pregnancy. There are no home remedies or over-the-counter drugs that will cure syphilis but syphilis is easy to cure in its early stages. Treatment during pregnancy should be with penicillin. The fetus can be easily cured with treatment and the risk of adverse outcomes to the fetus is minimal if the mother receives adequate treatment during early pregnancy ideally before the second trimester. The only exception is early syphilis diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy which should be treated with. Since the publication of the WHO Guidelines for the management of sexually transmitted infections in 2003 changes in the epidemiology of STIs and advancements in prevention diagnosis and treatment necessitate changes in STI management. Ultrasonography provides a noninvasive means to examine pregnant women for signs of fetal syphilis and abnormal findings indicate a risk for obstetric complications and fetal treatment failure. Azithromycin and ceftriaxone offer potential alternatives for penicillin-allergic women but insufficient data on efficacy limit their use in pregnancy.
68 70 Tetracycline the only other agent that has been proved effective is not recommended because of dental staining and impairment of long bone growth in the fetus and hepatotoxicity when given intravenously to a pregnant women with coexisting renal insufficiency. Thirty-three gravidas with syphilis were monitored with hourly vital signs and examinations for 24 hours after treatment with benzathine penicillin G. Ultrasonography provides a noninvasive means to examine pregnant women for signs of fetal syphilis and abnormal findings indicate a risk for obstetric complications and fetal treatment failure. Patients who are allergic to penicillin should be desensitised before treatment. In determining a penicillin regimen the clinician must consider the stage of the maternal infection and the HIV status of the mother. Syphilis in newborn children. Congenital syphilis after maternal treatment for syphilis during pregnancy.





























Post a Comment for "Syphilis Treatment In Pregnancy"