Interstitial Lung Disease Guidelines
Interstitial lung disease guidelines. 1-3 Although the etiology of. The interstitial lung diseases comprise a complex group of pulmonary disorders principally affecting the pulmonary interstitium. The British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society.
Sources and selection criteria. Pediatrics June 2016 137 6 e20152725. Up to 10 of people with RA are affected by interstitial lung disease ILD during their lifetime and ILD is one of the leading causes of death in patients with RA.
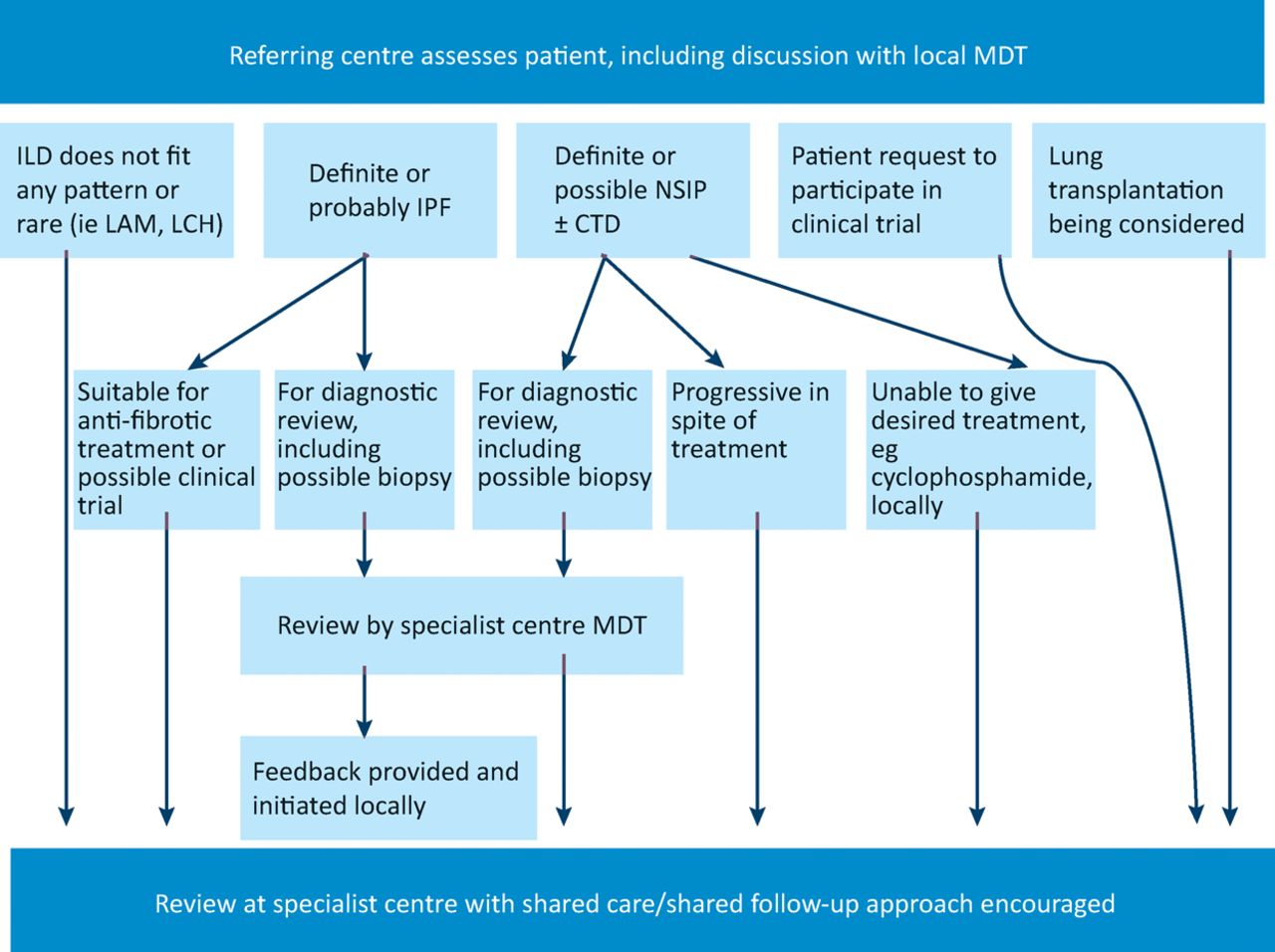
The British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society A U Wells1 N Hirani2 on behalf of the British Thoracic Society Interstitial Lung Disease Guideline Group a subgroup of the British Thoracic Society Standards of Care. Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. A Medical University Clinic Canton Hospital Baselland and University of.
CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report The evidence supporting the management of chronic cough in ILD is limited. Interstitial lung diseases are a group of diffuse parenchymal lung disorders associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. Interstitial lung disease ILD is a category of chronic lung disease that includes hundreds of conditions.
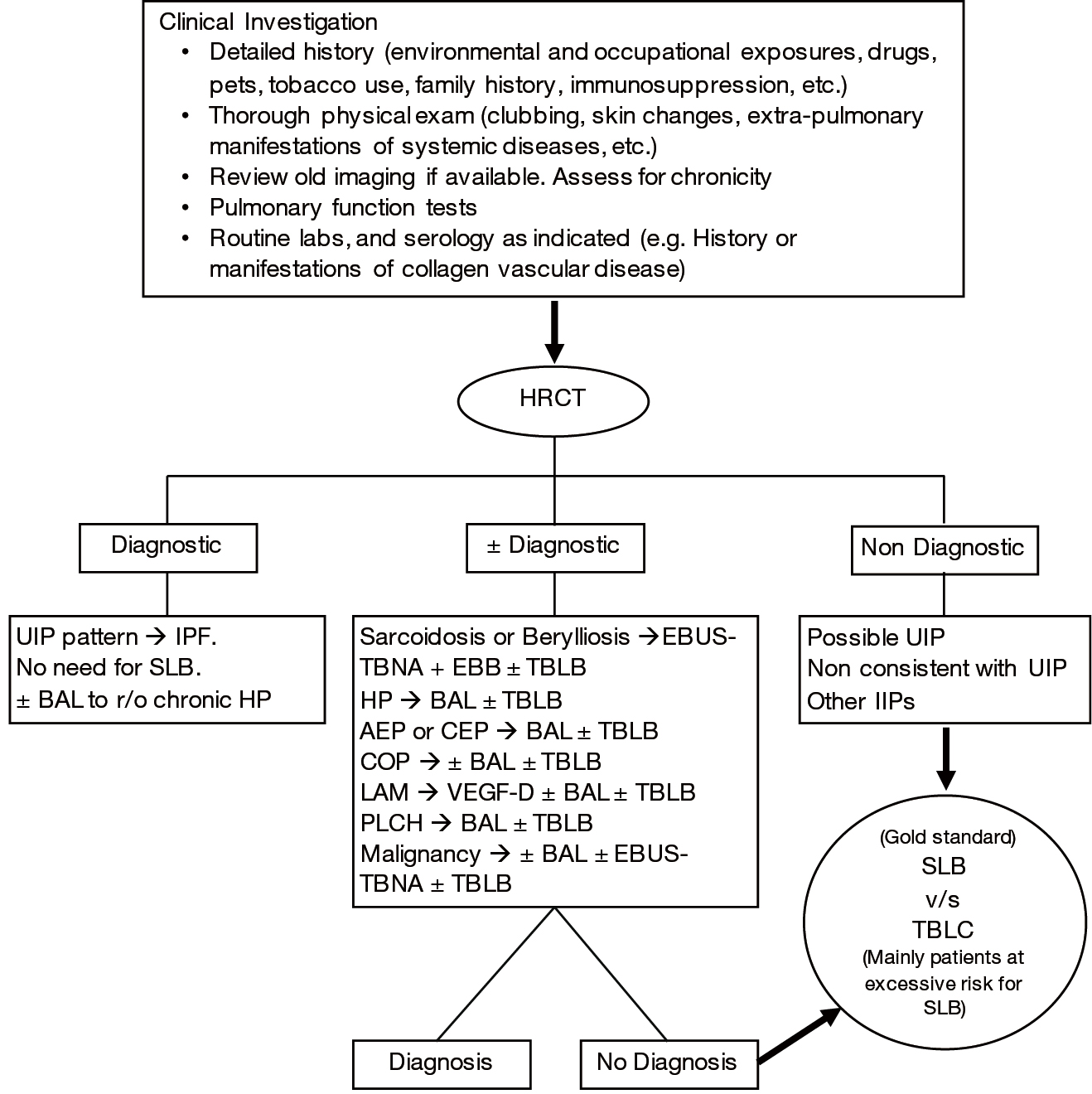
I n clinical practice respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease is increasingly diag-nosed without surgical lung biopsy in smokers on the basis of clinical and imaging features ground-glass opacities and. It also aims to protect staff from infection and enable services to make the best use of NHS resources. 2008 Sep63 Suppl 5v1-58doi.
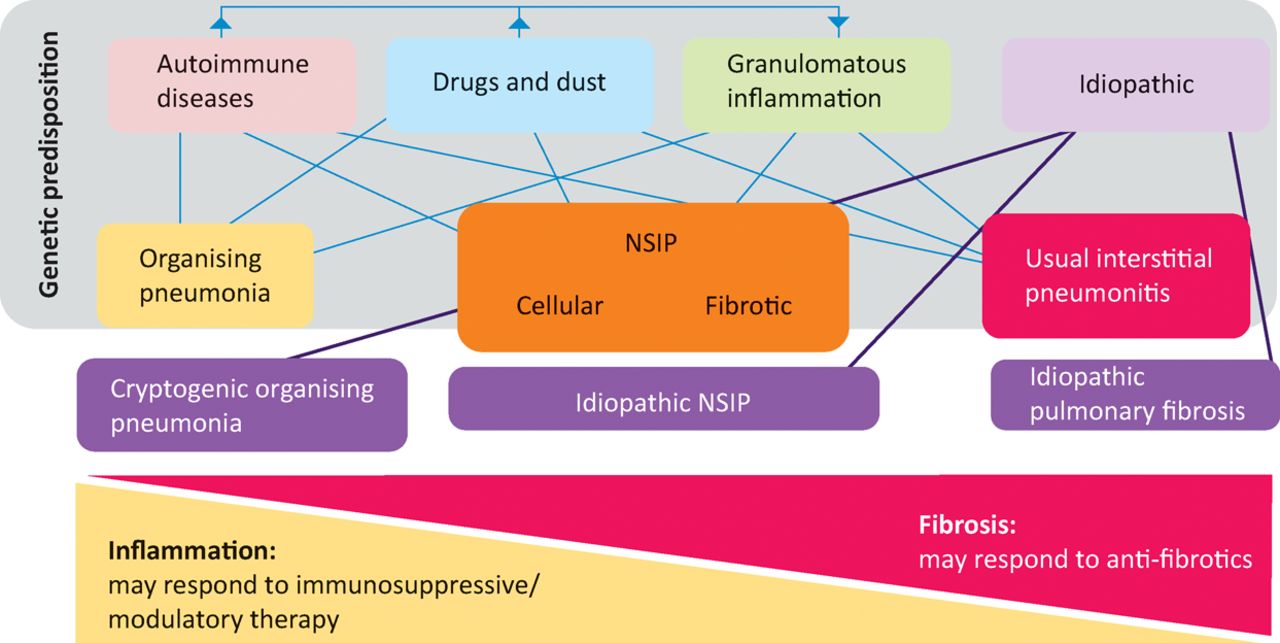
This guideline presents suggestions for managing and treating cough on the best available evidence but future research is. Interstitial lung disease ILD is a group of pulmonary dis- eases characterized by inflammation and fibrosis of the lung parenchyma1The diagnosis of fibrotic ILD is challenging with key diagnostic considerations described and recommen- dations provided in a recent Canadian Thoracic Society CTS Position Statement2The management of patients with ILD is also complex and must be multi-faceted. Untreated ILDs can lead to complications such as growth problems in children venous thromboembolism lung cancer.
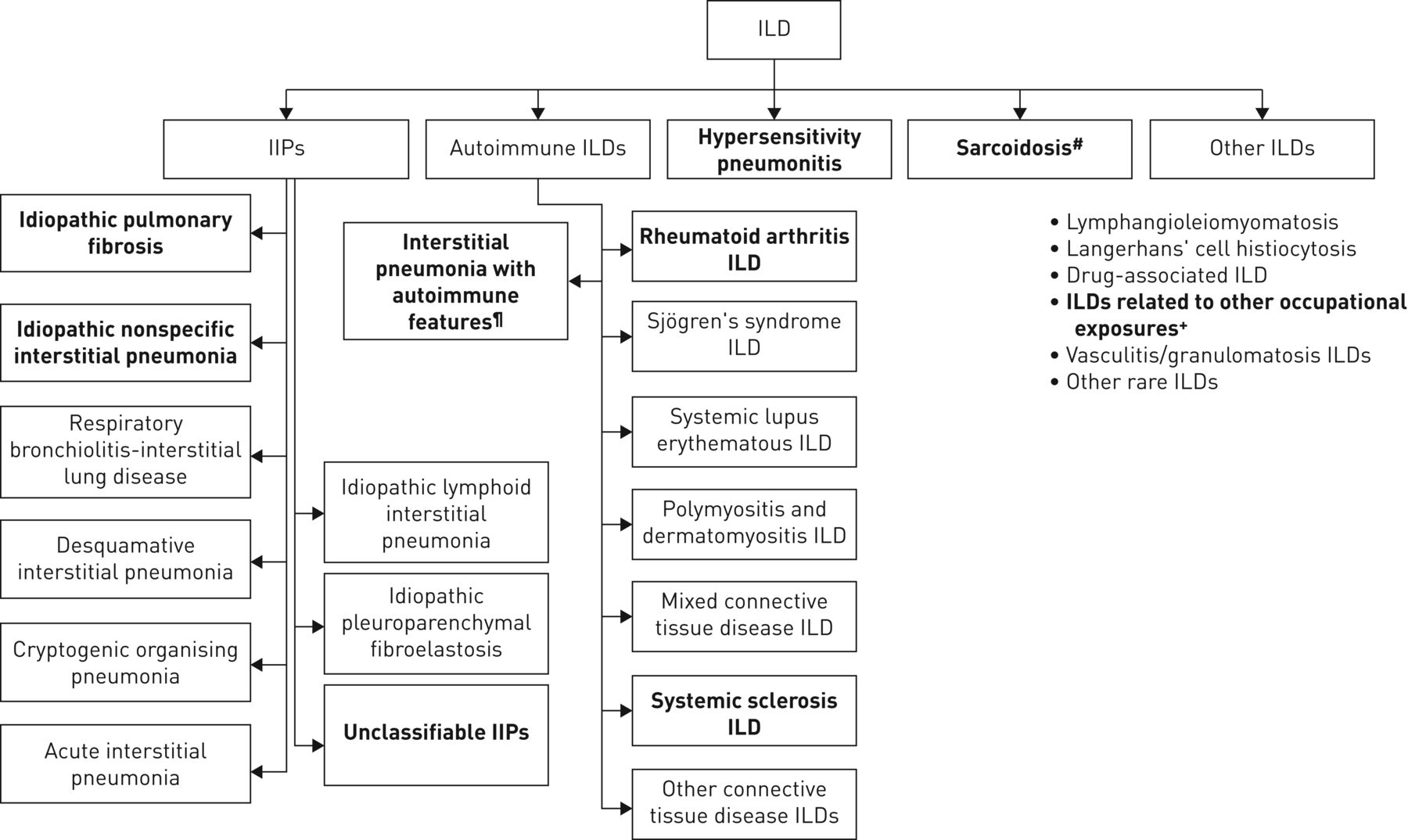
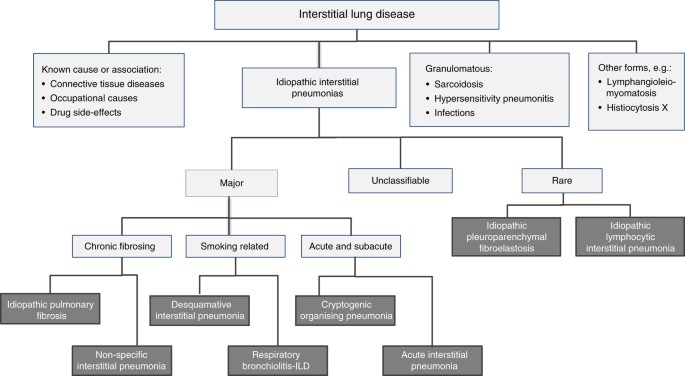
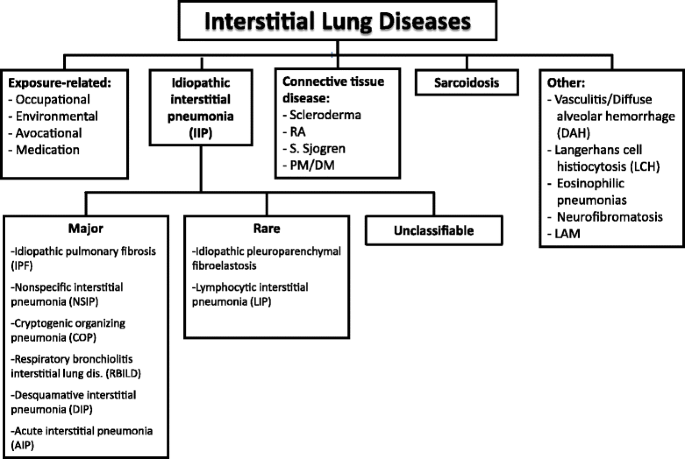
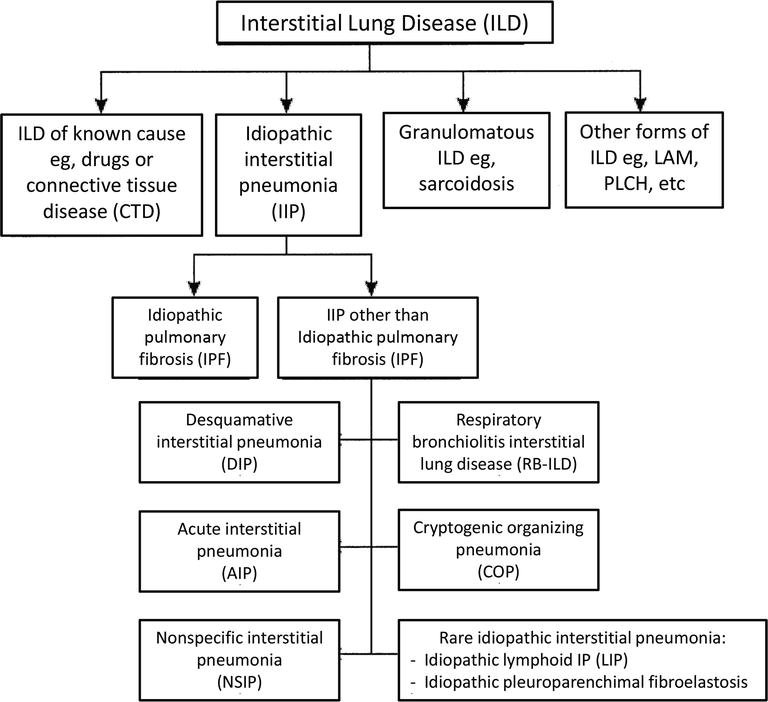
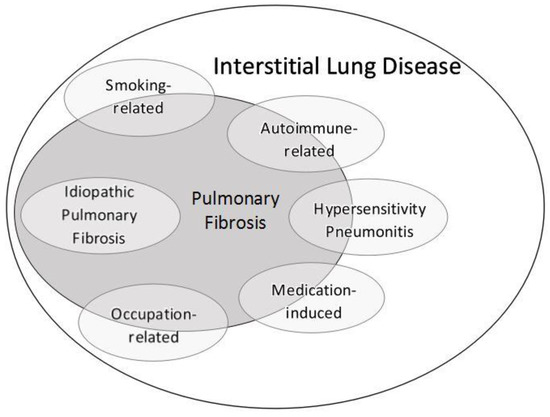
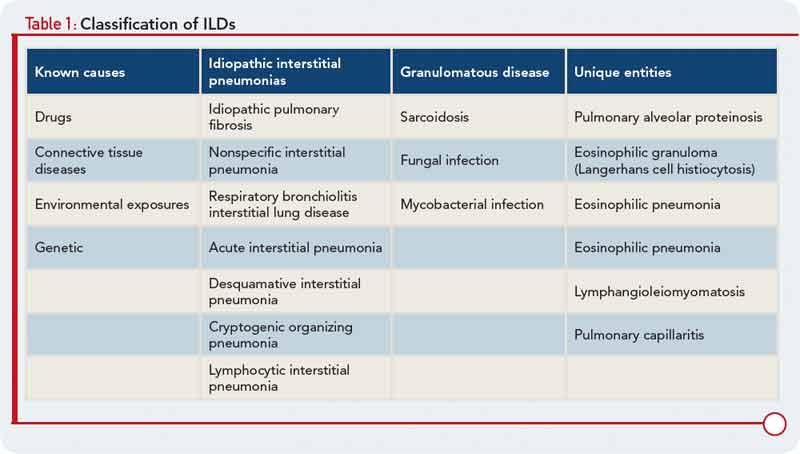
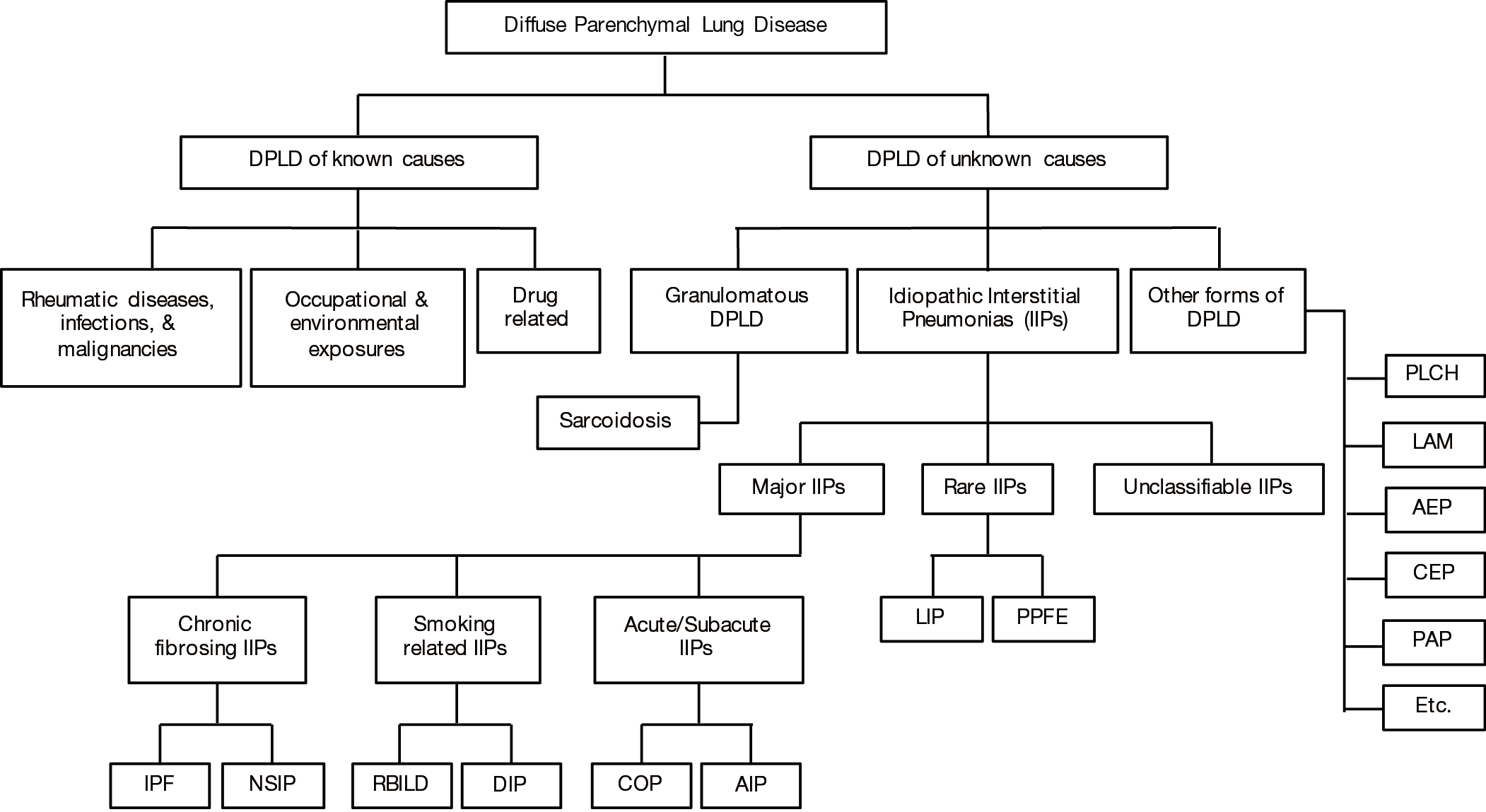
Risk factors include smoking and exposure to various environmental pollutants and contaminants like asbestos silica dust and coal. Knowledge achieved in recent years has resulted in the publication of the new classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias according to which there are three groups.
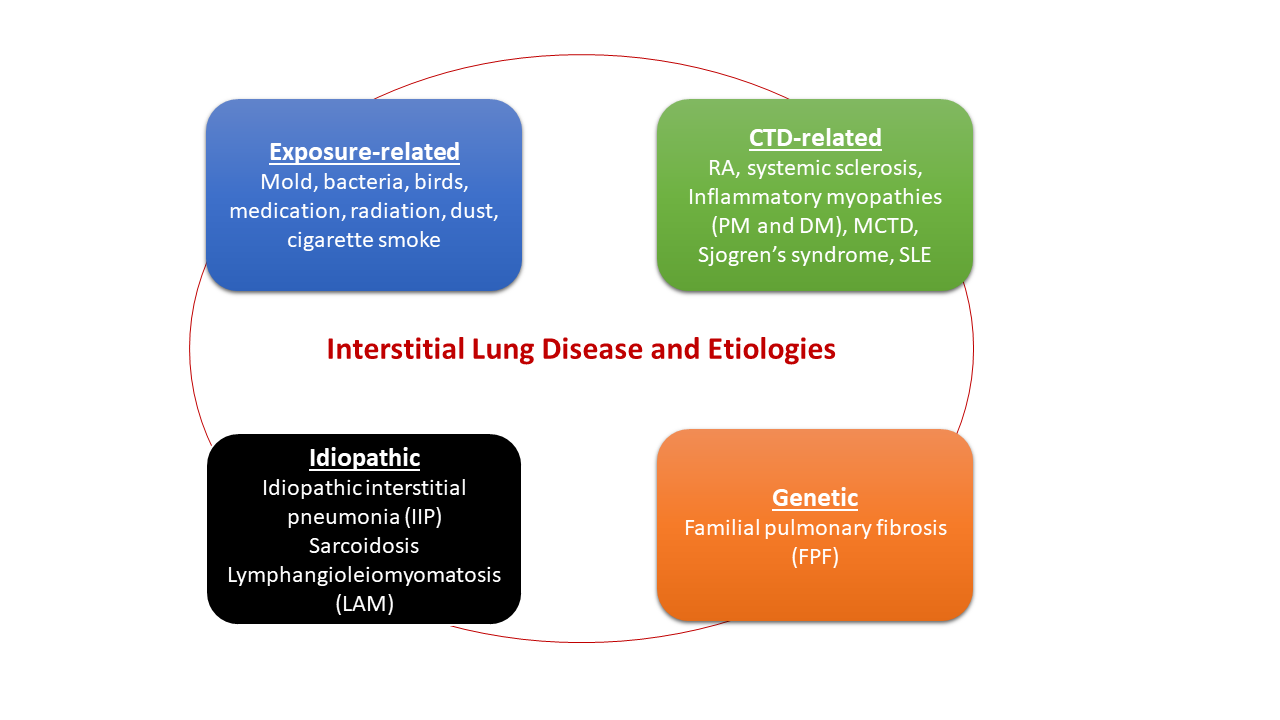
Idiopathic interstitial lung disease has no clear cause or contributing factor.
The British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Scarring in the lungs is often permanent but early diagnosis and treatment can help slow or stop the scarring. Up to 10 of people with RA are affected by interstitial lung disease ILD during their lifetime and ILD is one of the leading causes of death in patients with RA. I n clinical practice respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease is increasingly diag-nosed without surgical lung biopsy in smokers on the basis of clinical and imaging features ground-glass opacities and. 2008 Sep63 Suppl 5v1-58doi. Risk factors include smoking and exposure to various environmental pollutants and contaminants like asbestos silica dust and coal. Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Henderson-Hasselbalch equation and the relationship between partial pressure of oxygen PO2 partial pressure of carbon dioxide PCO2 and pH. The term interstitial lung disease is synonymous with diffuse parenchymal lung disease and while the latter was used in the 1999 BTS guideline a decision was made to adopt interstitial lung disease in the current document consistent with other international guidelines.
Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated Cough. Interstitial lung diseases are a group of diffuse parenchymal lung disorders associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. Untreated ILDs can lead to complications such as growth problems in children venous thromboembolism lung cancer. Occupational Interstitial Lung Disease Training Module If a given treatment or modality is not producing positive results the provider should either modify or discontinue the treatment regime. An Official ATSERSJRSALAT Statement 2011. Diagnosis of A-B disorders. An Official ATS Clinical Practice Guideline 2012 - Online Supplement Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.

















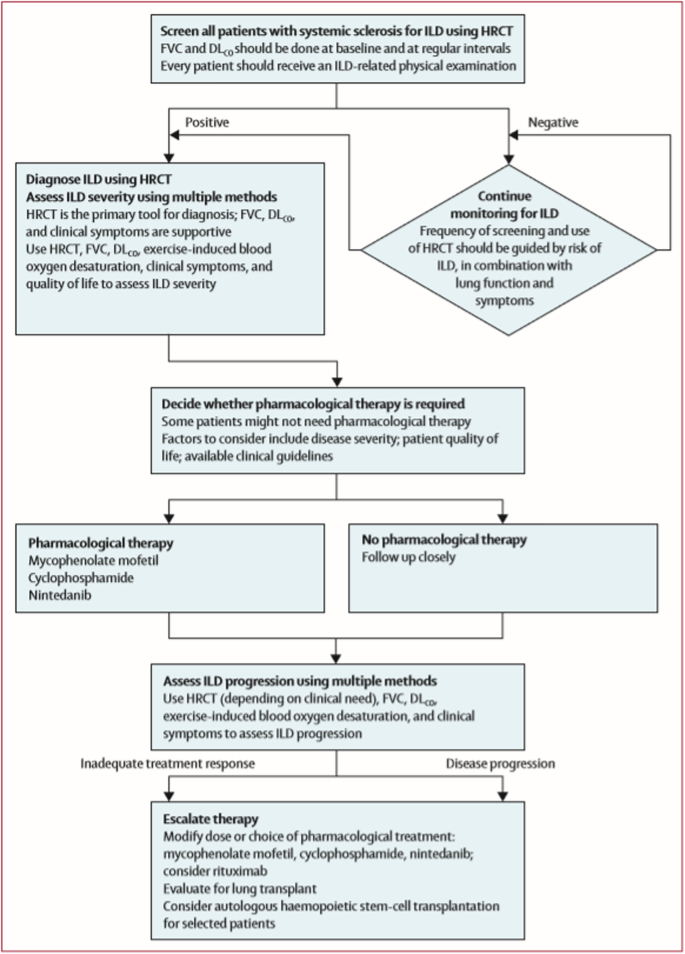
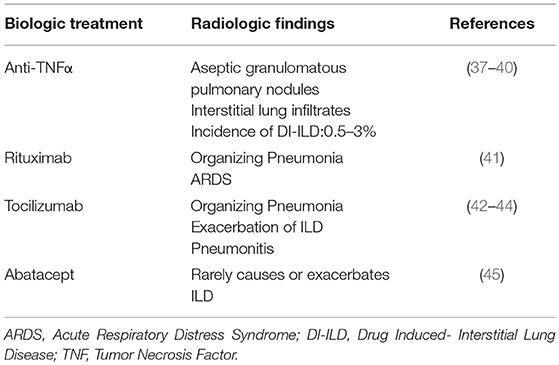




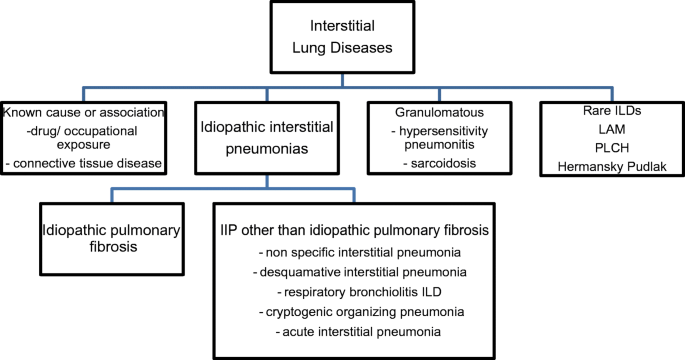
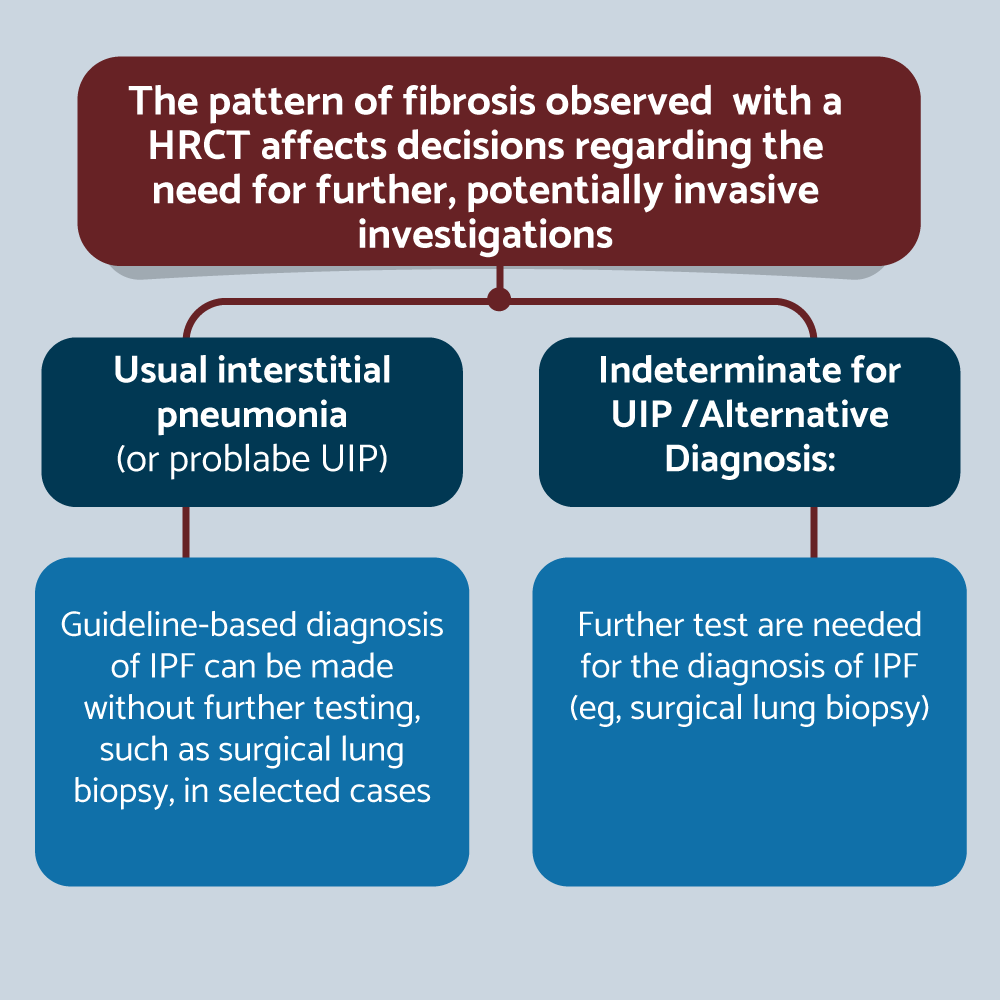












Post a Comment for "Interstitial Lung Disease Guidelines"